Bot vs. Bot: How Artificial Intelligence both drives and fights fraud
Dread it, run from it, Artificial Intelligence has arrived. Some experts are proclaiming that software utilizing AI could help eradicate diseases, cybersecurity threats, fraud, and even world hunger. Others warn that AI could have a huge negative impact on humanity, costing jobs, spurring fraud and chargebacks, and even fueling deadly wars. Ultimately, AI is a tool and whether it’s a positive or negative for human society may come down to how we use it. Still, there are plenty of risks to watch out for.
It’s hard to say what the future holds, but the below statement signed by numerous tech luminaries should undoubtedly give pause:
Mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority alongside other societal-scale risks such as pandemics and nuclear war.
Ultimately, AI is a vast, emerging field and we still can’t predict how it’ll transform the world. Many liken the transformative power of AI to the Internet, which fueled the spread of knowledge and instantaneous global communication and paved the way for online shopping, Software-as-a-Service, and more. However, the Internet also spurred the spread of computer viruses, misinformation, and has supercharged fraud, resulting in chargebacks, data breaches, and all the rest.
It’s hard to separate AI-perpetuated fraud from human-driven criminal activity. Still, the overall numbers are concerning. In 2022, the FTC’s Consumer Sentinel Network received over 5 million reports.
- Roughly 46% of the reports were for fraud.
- 21% were for identity theft.
- Credit card fraud accounted for over 40 percent of identity thefts.
- Miscellaneous identity theft at 28.1 percent, with social media, email, and account-related fraud especially common.
As criminals learn to use AI, these numbers will rise. Yet at the same time, AI will also provide tools for fighting crime. We’re going to cover some of the threats AI may pose to merchants. First, however, let’s step back to examine what may make AI so transformational, both for legitimate businesses and fraudsters.
Artificial Intelligence Increases Productivity
There’s a lot worth unpacking with AI. However, one could argue its most likely near-term impact is an increase in productivity. People can use AI to do much more with much less. For example, a retailer might use AI to automatically handle inquiries from customers or to analyze inventory in real-time with minimal need for human input.
Bad Robots: AI Software in the Hands of Fraudsters
Up until recently, many scams have relied on good old-fashioned people power, and as a result, scamming people took quite a bit of time. A fraudster might call up a target, chat them up on the phone with some yarn about forgotten debt or medical bills. From dialing to closing the “deal,” the fraudster will have to invest a lot of time. Fortunately, many people will catch onto the ruse and hang up, thus eating up the fraudster’s labor without rewarding them.
Now, fraudsters can use AI-generated voices to call people up, speak with them, and ultimately try to pressure them with various scammer tactics. Worse yet, some AI programs can even emulate a specific person’s voice. An AI scammer might pretend to be your child or spouse, for example, and beg for money. While many people will recognize scammers who are unknown or have an odd accent, hearing a loved one’s voice can quickly ratchet up the pressure.
At the end of the day, AI is going to increase productivity. Unfortunately, that potential proves true for criminals as well. Let’s look at some more specific ways AI could endanger both consumers and businesses.
Fake Identities
Fraudsters are using AI to gather data, such as names and addresses, and then to create fake or fraudulent IDs. It’s possible to mix legitimate info with wholly made-up data to create fraudulent identities that are difficult to pick out. However, robust monitoring programs, including ones that use AI, may be able to uncover fraudulent IDs before transactions are completed. This could reduce fraudulent transactions and chargebacks, among other things.
Fraudulent Emails
Chatbots can write text for you using Natural Language Processing models. Essentially, AI chatbots have been trained to write in a language that sounds like our own. This means fraudsters can use AI to write messages, such as phishing letters. A phishing letter will try to get people, such as cardholders, to hand over sensitive information, like credit card numbers.
Writing these emails used to be time-consuming. Yet with an AI-powered chatbot, cybercriminals can write human-sounding emails in seconds. Fraudsters who might have spent a week writing out various phishing emails can now crank out a bunch in a matter of minutes.
Check out this example for ChatGPT:
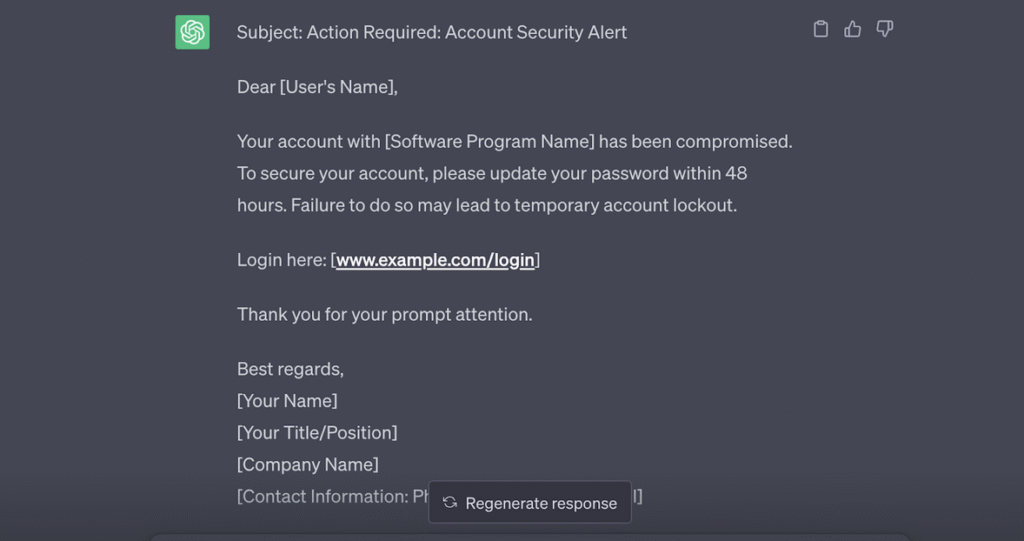
Sounds official, right? Yet the only thing a fraudster needs to do to turn this into a phishing email is to simply include a malicious link in the [www.example.com/login] field. With that link, a hacker could send you to an official-looking portal, for example, that prompts you to type in your password. From there, the fraudsters could take over an account, then make unauthorized purchases. Shortly after, merchants may end up dealing with chargebacks and irate customers.
Using AI Chatbot Software to Talk With Targets
Companies now offer chat services that you can utilize to chat with customer service. You might message your bank to get help activating a new credit card, for example. Or you might contact a merchant to ask for an update on your order. Many of these chat programs use AI to handle various requests, and they can be as effective as their human counterparts.
Indeed, these AI chatbots can dramatically increase response times while helping companies manage the cost of their customer service department. Unfortunately, they offer the same benefits to hackers. Personally chatting with someone, trying to convince them to hand over a credit card number, eats up time. If a bot can do the work, however, it’s suddenly possible to target essentially an unlimited number of people.
Of course, if hackers should get credit card numbers or other sensitive data, this could lead to fraudulent transactions, chargebacks, and other headaches.
Fraudulent AI Apps and Extensions
AI-powered extensions and apps are quite popular at the moment. Many organizations and individuals are leveraging AI, mostly for good, and thus they’re downloading AI-powered apps and software. Most of the apps are probably legitimate, but some hackers have been embedding malicious code into the apps.
If a retailer downloads a malicious app, the app may steal sensitive data, such as a customer’s account information. Once the data is delivered to fraudsters, they might use it to make fraudulent purchases, including from the originally targeted merchant. Later on, retailers could find themselves dealing with chargebacks from these transactions.
When downloading apps, it’s wise to only download from trusted resources. It doesn’t matter what type of software you’re using, a simple task manager, a browser extension that helps you find coupons, dispute management platforms, whatever: make sure it’s coming from a reputable source. And by source, we don’t simply mean using the official Apple App Store or Google Play. Unfortunately, malicious software makes it into these platforms as well.
When selecting software, it’s smart to look at the developer. You’ll want to work with reputable companies and developers who have a long track record. Fore example, if you’re looking for an Amazon app, make sure it’s distributed by Amazon itself, and not some shady developer that put Amazon in the app title. Software that has been in use for a while may also be safer than newer software.
Good Robots: How AI Can Help Fight Back
The tech industry has been facing skill shortages for years and anyone with the skills to hack into a platform could likely land a high-paying job. This talent crunch has left cyber-criminal groups short on labor power and trying to scam people by finding gaps in code has traditionally taken a lot of work. Now, AI can be used to analyze and test code, potentially uncovering security gaps that can be exploited.
AI Can Uncover Zero Day Exploits
The most dangerous exploits are typically so-called “Zero Day” exploits. These are vulnerabilities in code that no one knows about, which means the door is left wide open. Since the developer has no warning, they have “zero” days to fix it, hence the name. Some of the most devastating cybersecurity attacks in history were the result of zero-day exploits.
These days, companies and developers take cybersecurity very seriously. As a result, well-programmed software is often resistant to attacks. Vulnerabilities still exist, but hackers may have to spend hours upon hours sifting through code, hoping to get lucky. At least, that’s been standard practice up until now.
AI has made it easier to quickly analyze code to uncover vulnerabilities. Many cybersecurity companies and developers at technology companies are also using AI to analyze their code, however. When vulnerabilities are found, the software can be patched, thus closing the gap. Used appropriately, AI can make software safer.
Conversely, bad actors already use AI to find gaps that they can exploit. AI is a tool, it can’t think, so it’s not personally perpetuating the crime. Yet hackers using AI have now set off an arms race, the goal being to find zero-day exploits.
When selecting software platforms, including chargeback and dispute management software, it’s wise to work with companies that take cybersecurity seriously.
Artificial Intelligence Could Supercharge Cybersecurity
The good news is, many ethical hackers and other “white hats” are using AI to combat cybersecurity fraud, including account takeovers, misused credit/debit cards, and much more. Not only could this help reduce financial fraud in general, but it could also lead to reduced chargebacks.
One powerful way to reduce fraud is through behavioral fraud detection, for example. Essentially, you’ll closely analyze the behavior of both customers and scammers, then identify patterns that allow you to distinguish between the two. At a basic level, this can be quite simple. If a customer who lives in Florida is suddenly ordering something and having it shipped to Oregon, it may be because a scammer based in Oregon is misusing their credit card or account.
CONCLUSION
Amid the AI arms race, it’s important for businesses to be proactive. Effective cybersecurity protocols will mitigate risks. It’s also crucial to keep a close eye on finances and to reduce things like chargebacks that hack into your bottom line. As AI drives innovation, markets may grow more competitive. If you’re shelling out money and wasting labor fighting fraud and chargebacks, it could erode your competitive position. Yet those companies that leverage AI properly and that use effective dispute management platforms to combat fraud and chargebacks could come out ahead.








